| Alternative names | N/A |
| Known ligands | N/A |
| Origin | Homo sapiens |
| Accession number | Q7Z7D3 |
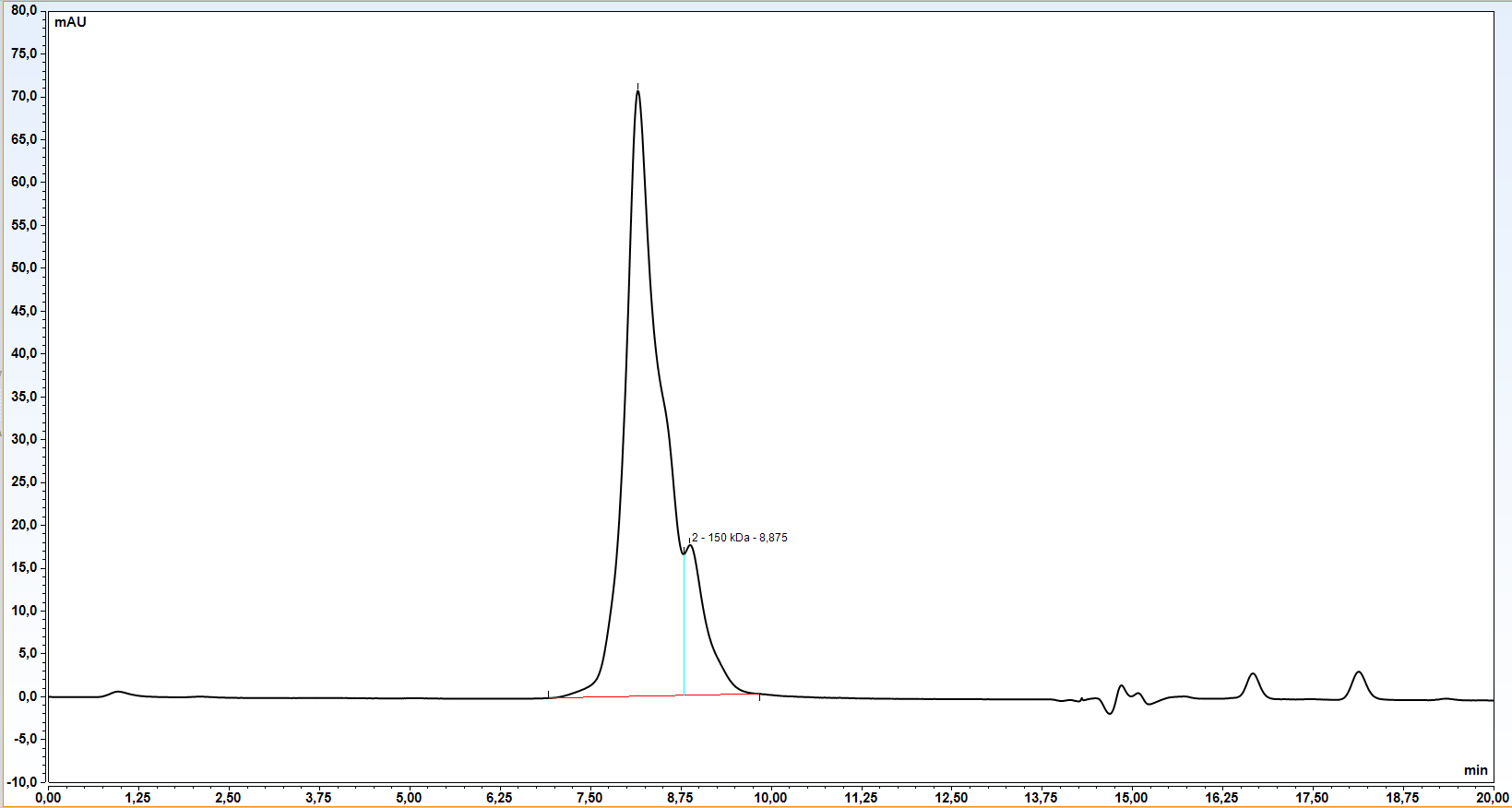
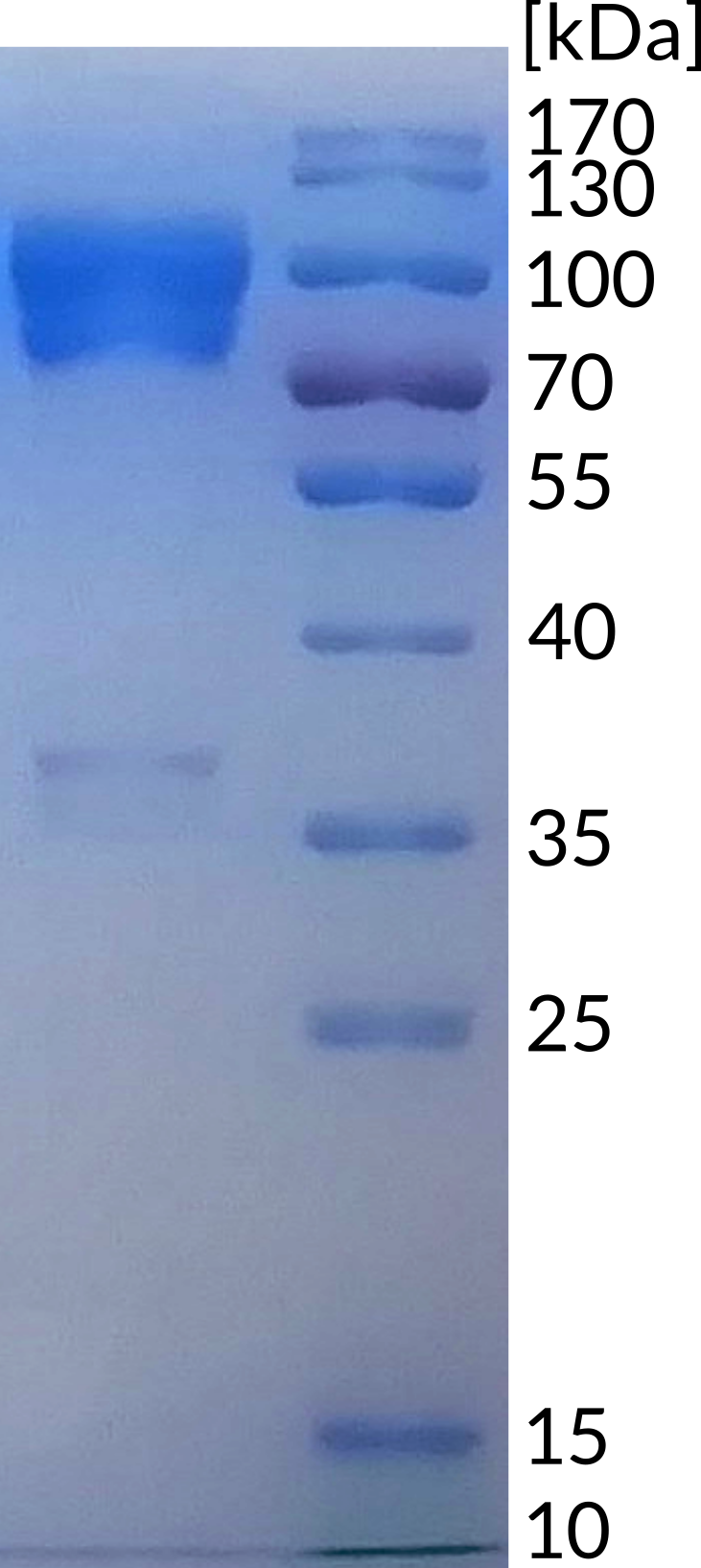

B7-H4 is type-I transmembrane protein, sharing only about 25% homology with ther B7 family members (1). While its RNA is found in almost every normal tissue, presence of the protein on cell surface is extremely limited, but can be induced on T cells, B cells, monocytes and dendritic cells by stimulation (2). It is also expressed by various cancer cells and its presence on tumors (e.g. in ovarian cancer) is directly related to cancer characteristics as well as patient survival (3), therefore making it potential target for immune checkpoint blockade. Binding of B7-H4 to its receptor (so far not identified) results in arresting the cell cycle, which consequently leads to inhibition of CD4+ and CD8+ T-cell proliferation, cytokine production and generation of alloreactive cytotoxic T-cell lymphocytes (4).
- Zang, X., Kim, J., Murphy, K., Waitz, R., & Allison, J. P. (2003). B7x: a widely expressed B7 family member that inhibits T cell activation. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 100(18), 10388-10392.
- Sica, G. L., Choi, I. H., Zhu, G., Tamada, K., Wang, S. D., Tamura, H., … & Chen, L. (2003). B7-H4, a molecule of the B7 family, negatively regulates T cell immunity. Immunity, 18(6), 849-861.
- Podojil, J. R., & Miller, S. D. (2017). Potential targeting of B7‐H4 for the treatment of cancer. Immunological reviews, 276(1), 40-51.
- Prasad, D. V., Richards, S., Mai, X. M., & Dong, C. (2003). B7S1, a novel B7 family member that negatively regulates T cell activation. Immunity, 18(6), 863-873.
