Inducible T-cell costimulator
ICOS
| Alternative names |
AILIM |
| Known ligands |
ICOSL |
| Origin |
Homo sapiens |
| Accession number |
Q9Y6W8 |
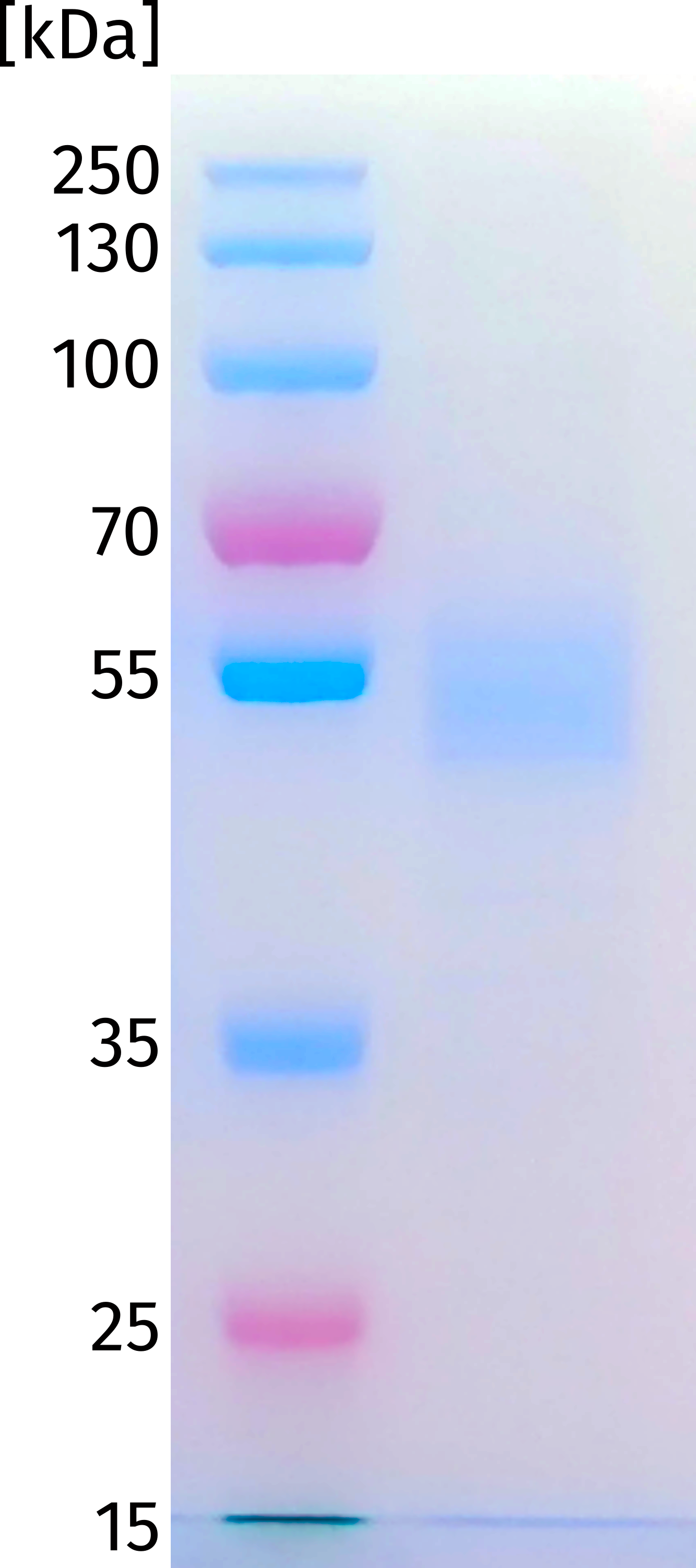
| R1-019-1 |
ICOS ECD (21 - 140) |
Fc-tag |
CHO |
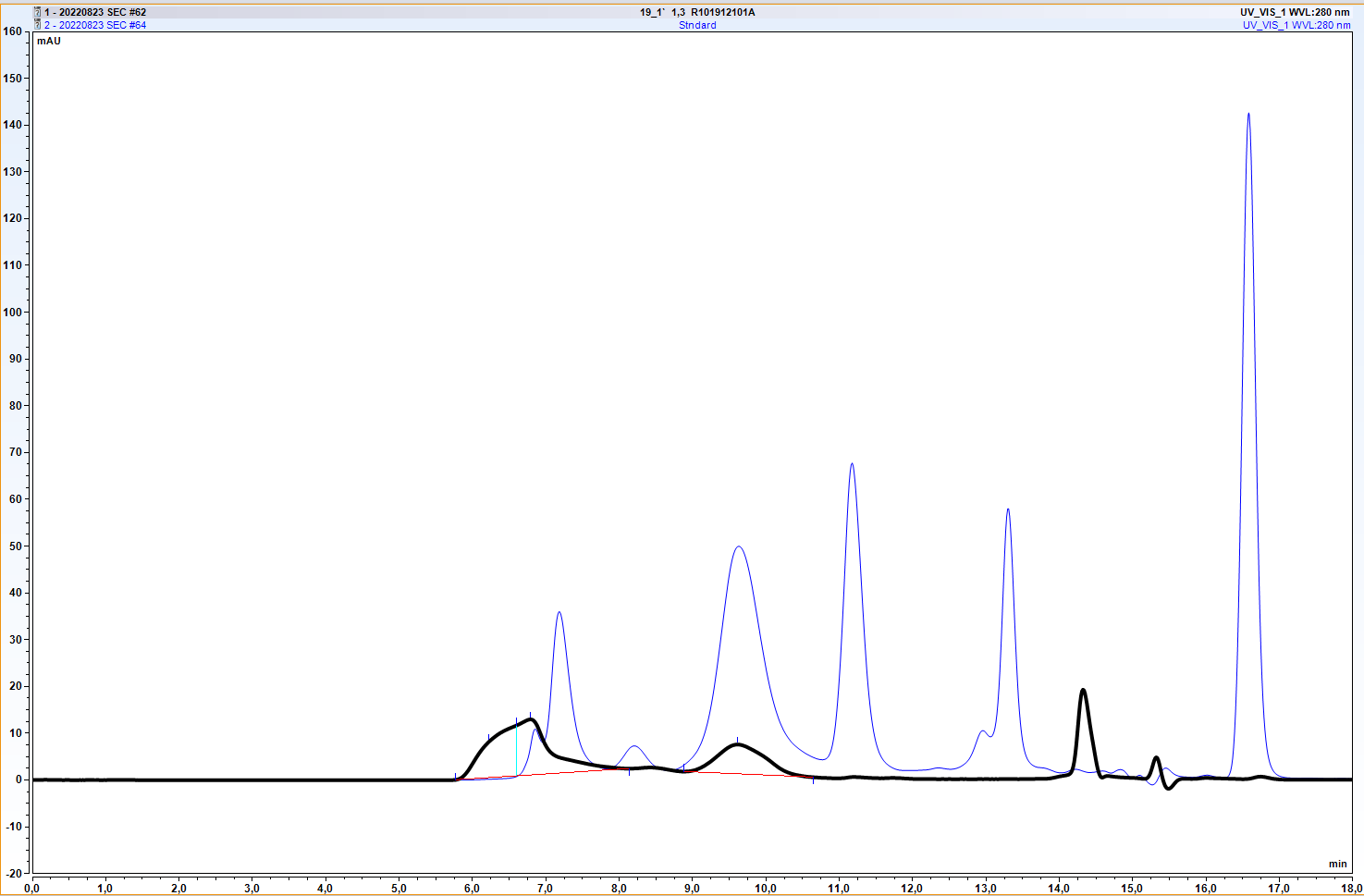
Yes |
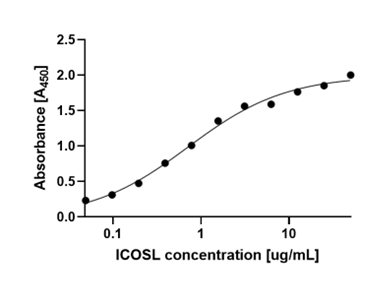
ELISA, WB, functional studies |
ORDER NOW
Inducible co-stimulator (ICOS), also called AILIM (activation-inducible lymphocyte immunomediatory molecule) and CRP-1 (CD28-related protein-1), is a cell-surface receptor and belongs to the CD28 family of immune costimulatory receptors consisting of CD28, CTLA-4, and PD-1 (1). Human ICOS is a homodimeric type I transmembrane protein consisting of 199 amino acids (aa). ICOS shares approximately 39% amino acid similarity with CD28 and CTLA-4. On the whole, ICOS co-stimulation supports a remarkable number of distinct processes during adaptive immune responses. By promoting the induction , maintenance, and follicular homing of Tfh cells, ICOS promotes TD Ab responses and drives Ab affinity maturation in the GC reaction. Additionally, ICOS serves to enhance or dampen Th1 and Th2 inflammatory responses, depending on the given pathogen (2). Signaling through the ICOS pathway is initiated once the ICOS protein interacts with its ligand, ICOSL (B7h, B7RP-1, CD275). Resting T cells express low levels of ICOS protein. Once the T cells are activated, the protein is rapidly upregulated. Upon activation, ICOS initiates a cascade of events that can shape key aspects of the immune response. It enhances T-Cell proliferation, lymphokines secretion and up-regulation of molecules involved in cell-cell interaction. CD278 prevents the apoptosis of pre-activated T-Cells. It plays a critical role in CD40-mediated class switching of immunoglobulin isotypes.
Depending on the context of inflammatory response, ICOS can also induce Th1, Th17 and T follicular helper (Tfh) response. ICOS protein also promotes B-Cell proliferation, differentiation into plasma and B-Cell antibody secretion.
ICOS protein is expressed at low levels in the lung, lymph node, thymus, peripheral blood leukocytes and in the medulla of the fetal and newborn thymus (3).
- Amatore F, Gorvel L, Olive D. Role of Inducible Co-Stimulator (ICOS) in cancer immunotherapy. Expert Opin Biol Ther. 2020 Feb;20(2):141-150. doi: 10.1080/14712598.2020.1693540. Epub 2019 Nov 28. PMID: 31738626.
- Wikenheiser DJ, Stumhofer JS. ICOS Co-Stimulation: Friend or Foe? Front Immunol. 2016 Aug 10;7:304. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2016.00304. PMID: 27559335; PMCID: PMC4979228.
- Wikenheiser DJ, Ghosh D, Kennedy B, Stumhofer JS. The Costimulatory Molecule ICOS Regulates Host Th1 and Follicular Th Cell Differentiation in Response to Plasmodium chabaudi chabaudi AS Infection. J Immunol. 2016 Jan 15;196(2):778-91. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1403206. Epub 2015 Dec 14. PMID: 26667167; PMCID: PMC4705592.