| Alternative names | CD275 |
| Known ligands | ICOS |
| Origin | Homo sapiens |
| Accession number | O75144 |
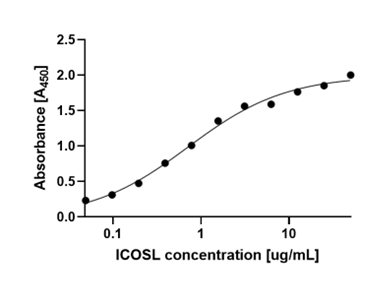
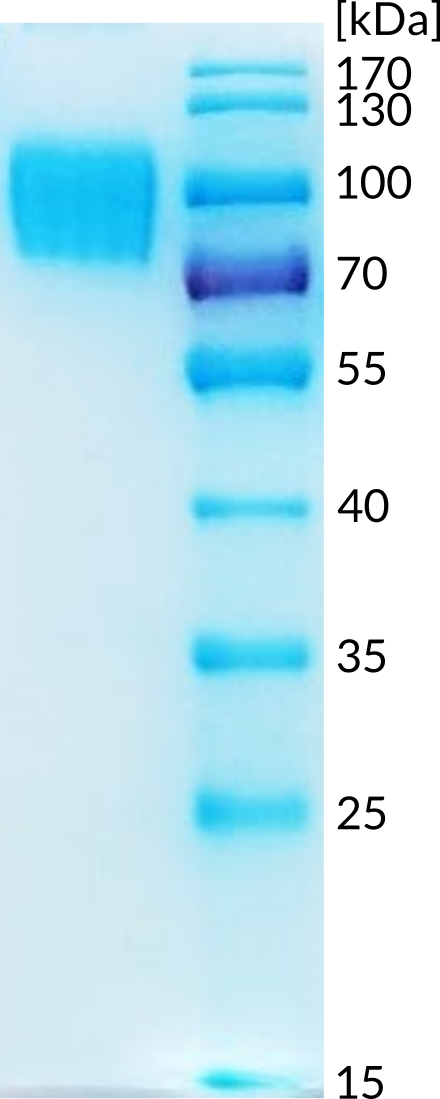
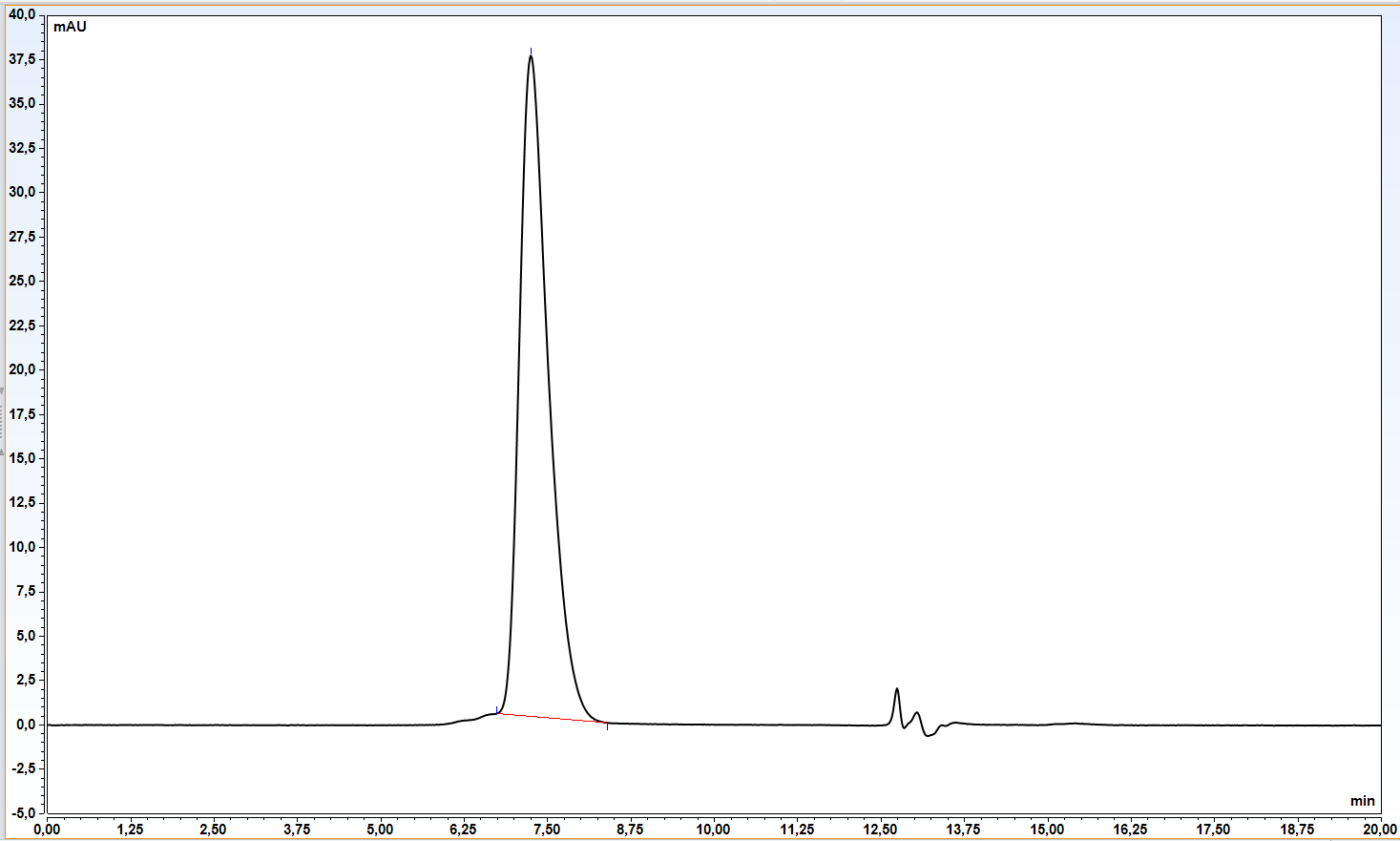

ICOS ligand is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ICOSLG gene. ICOSLG has also been designated as CD275. Inducible costimulator (ICOS) ligand (ICOSL) is a B7-related transmembrane glycoprotein with extracellular IgV and IgC domains. ICOS binds to a specific ligand on antigen-presenting cells and cells of the peripheral tissue different from the CD28/CD152 ligands CD80 and CD86. Acts as a costimulatory signal for T-cell proliferation and cytokine secretion; induces also B-cell proliferation and differentiation into plasma cells. Could play an important role in mediating local tissue responses to inflammatory conditions, as well as in modulating the secondary immune response by co-stimulating memory T-cell function (1). Diseases associated with ICOSLG include Autoimmune Disease Of Exocrine System and Immune System Disease. Among its related pathways are ICos-ICosL Pathway in T-Helper Cell and Innate Immune System.
- Chattopadhyay K, Bhatia S, Fiser A, Almo SC, Nathenson SG. Structural basis of inducible costimulator ligand costimulatory function: determination of the cell surface oligomeric state and functional mapping of the receptor binding site of the protein. J Immunol. 2006 Sep 15;177(6):3920-9. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.177.6.3920. PMID: 16951355.
