| Alternative names | N/A |
| Known ligands | N/A |
| Origin | Homo sapiens |
| Accession number | Q5ZPR3 |
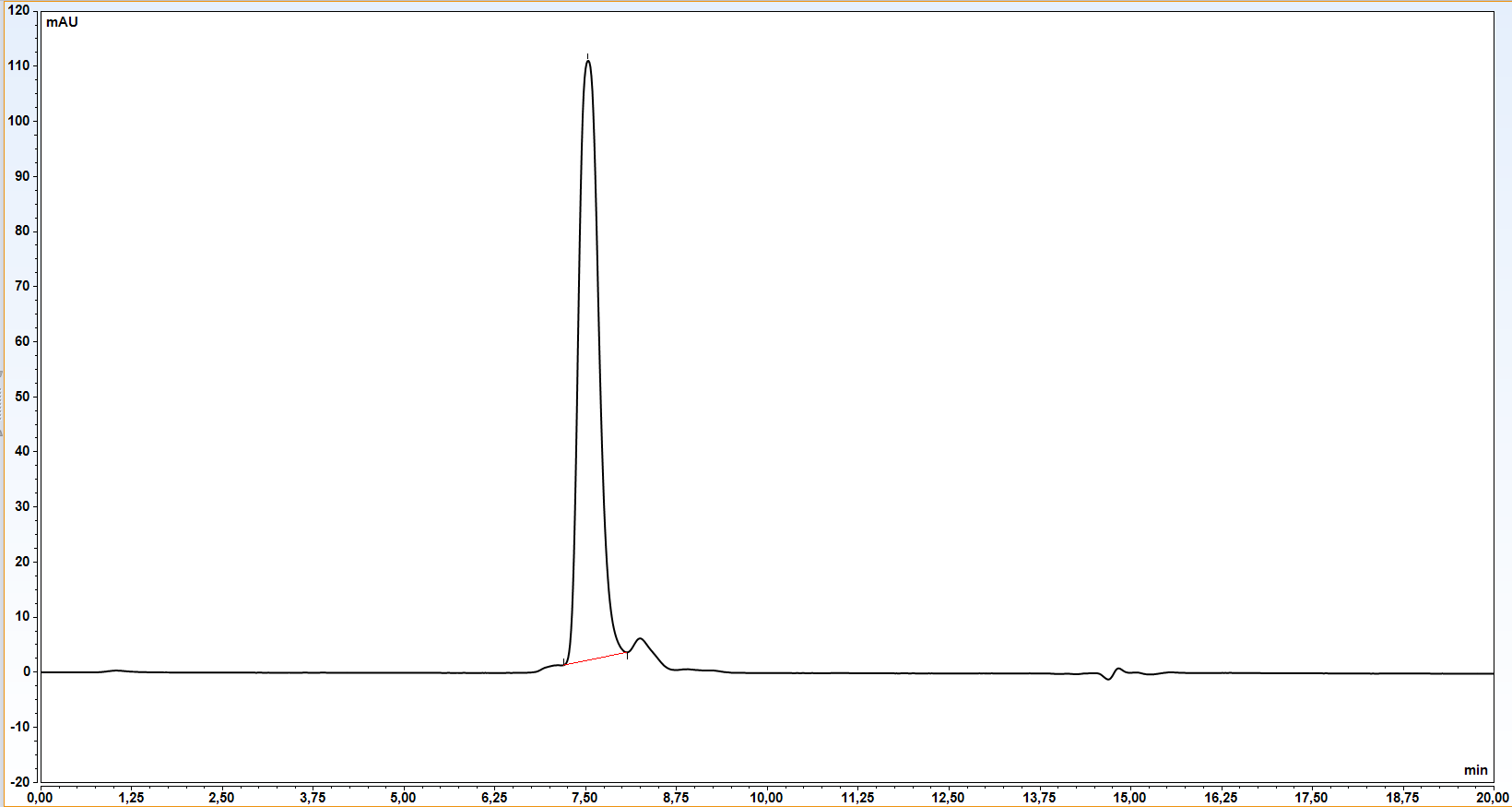
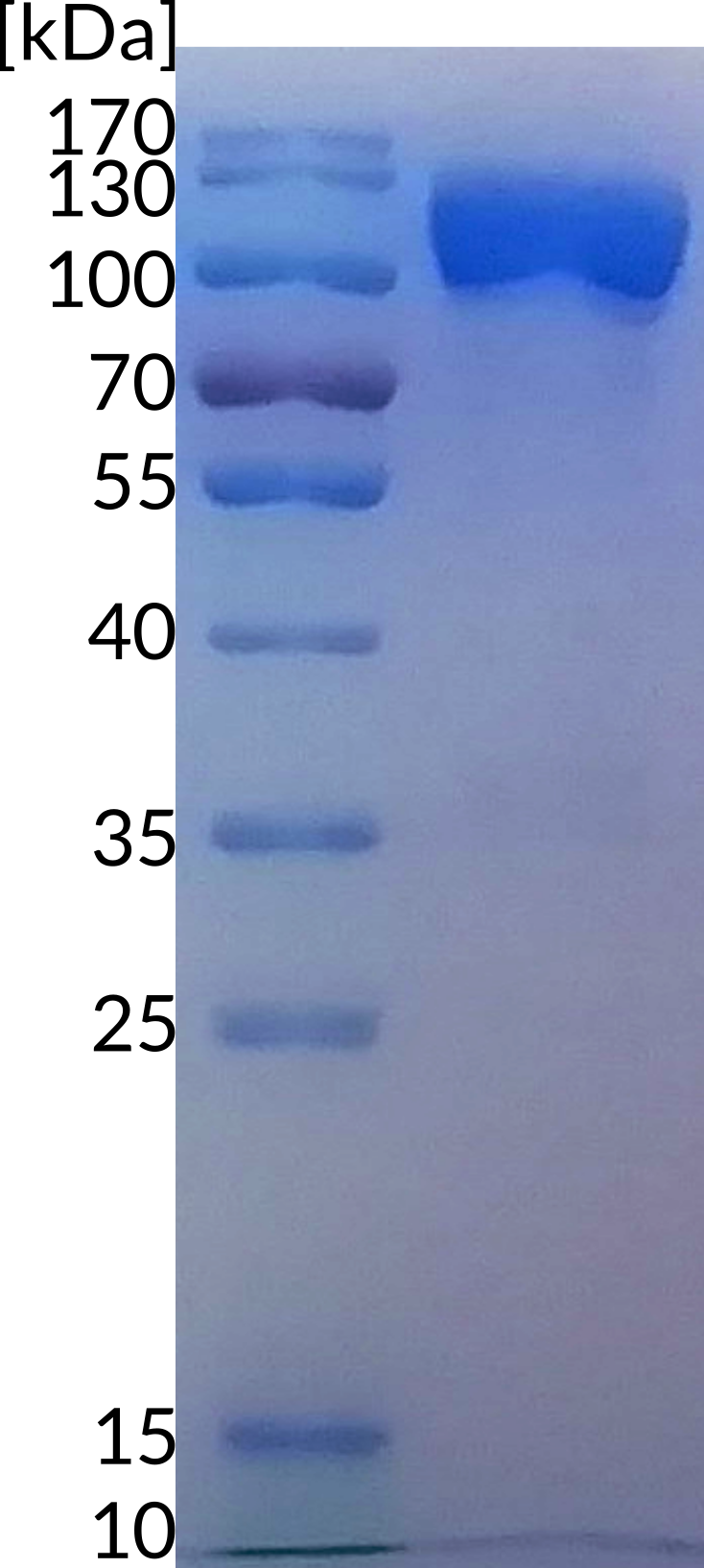

B7-H3 member of B7 family of molecules, responsible for inhibiting T-cells activity and therefore for tumor cell immune evasion (1). It consists of IgC and IgV domain, with FG loop on IgV playing critical role in its inhibitory effect (2). So far, the receptor binding B7-H3 has not been identified. B7-H3 is responsible for numerous phanomenon in tumor progression – besides immune evasion it also plays a role in invasion, migration, angiogenesis and gene regulation, which makes it highly versatile and potent target for cancer immunotherapy (1). B7-H3 mRNA is abundant in most normal tissues, with tigh post-transcriptional control, resulting in low level of protein on the cell surface. It is inducible on T-cells, NK cells, dendritic cells and macrophages (3).
- Castellanos, J. R., Purvis, I. J., Labak, C. M., Guda, M. R., Tsung, A. J., Velpula, K. K., & Asuthkar, S. (2017). B7-H3 role in the immune landscape of cancer. American journal of clinical and experimental immunology, 6(4), 66.
- Vigdorovich, V., Ramagopal, U. A., Lázár-Molnár, E., Sylvestre, E., Lee, J. S., Hofmeyer, K. A., … & Almo, S. C. (2013). Structure and T cell inhibition properties of B7 family member, B7-H3. Structure, 21(5), 707-717.
- Yi, K. H., & Chen, L. (2009). Fine tuning the immune response through B7‐H3 and B7‐H4. Immunological reviews, 229(1), 145-151.
