| Alternative names | N/A |
| Known ligands | CD70 |
| Origin | Homo sapiens |
| Accession number | P26842 |
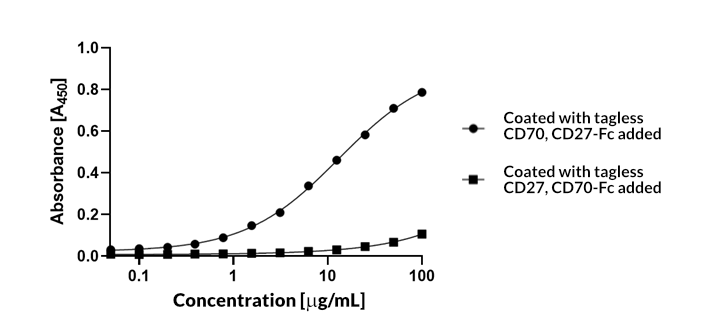

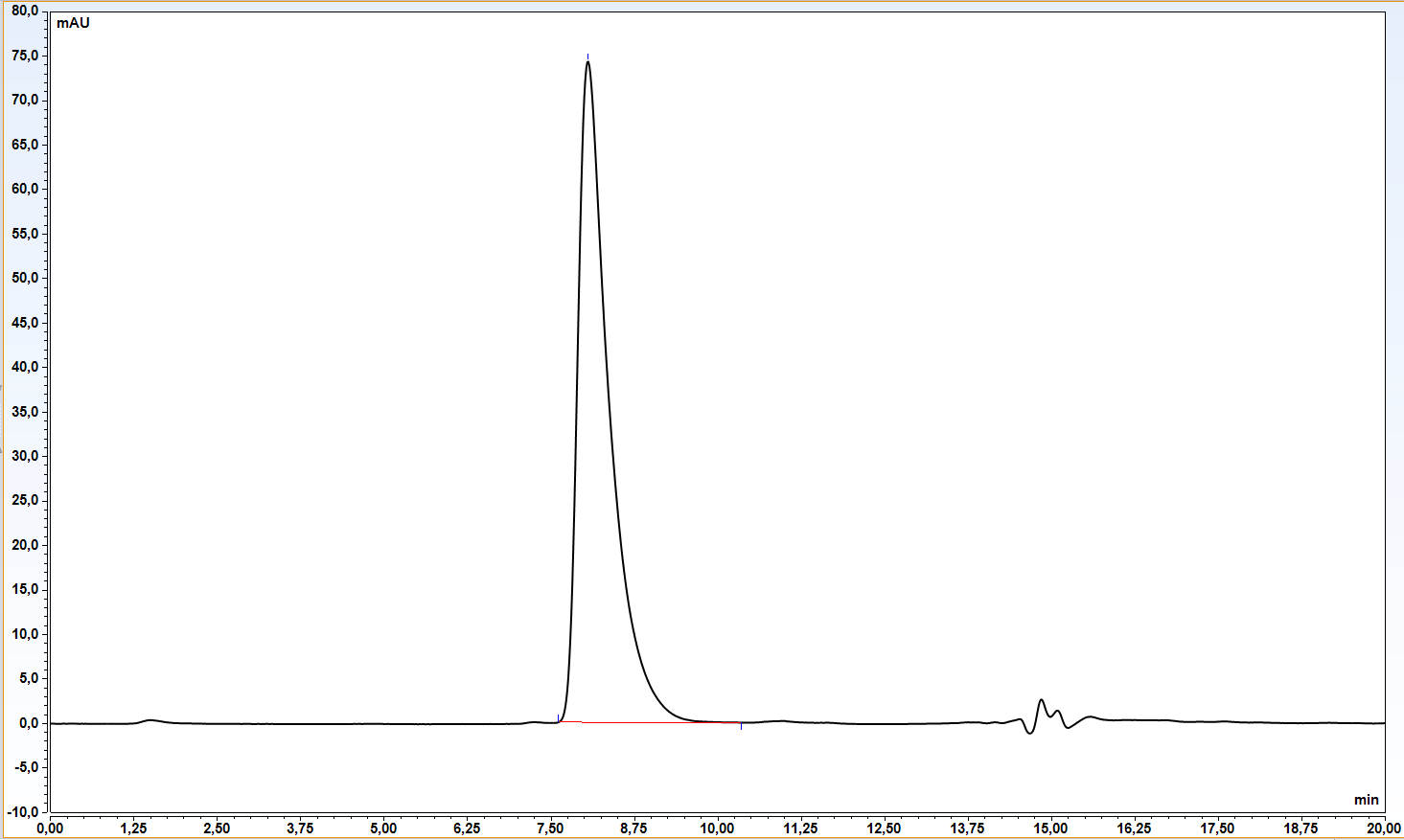

Human CD27 is a 260 amino acid (aa) protein with a 20 aa signal, a 173 aa extracellular domain, a 20 aa transmembrane domain, and a 47 aa cytoplasmic domain. CD27 is a glycosylated, type I transmembrane protein of about 55 kD and exists as homodimers with a disulfide bridge linking the 2 monomers. The disulfide bridge is in the extracellular domain close to the membrane. CD27 is a member of the tumor necrosis factor receptor (TFNR) superfamily. These receptors play an important role in cell growth and differentiation, as well as in apoptosis or programmed cell death. The homology of the TNFR gene superfamily is restricted to the extracellular region of the family members and is characterized by the presence of a Cys knot motif, which occurs 3 times in CD27 (2). The ligand for CD27 is CD70, which belongs to the tumor necrosis factor (TNF) family of ligands.
- D Camerini, G Walz, W A Loenen, J Borst, B Seed, The T cell activation antigen CD27 is a member of the nerve growth factor/tumor necrosis factor receptor gene family.The Journal of Immunology November 1, 1991, 147 (9) 3165-3169;
- Prasad, K. V. S., Ao, Z., Yoon, Y., Wu, M. X., Rizk, M., Jacquot, S., Schlossman, S. F. CD27, a member of the tumor necrosis factor receptor family, induces apoptosis and binds to Siva, a proapoptotic protein. Nat. Acad. Sci. 94: 6346-6351, 1997.
